Winter Weather Trends: El Niño in New Jersey
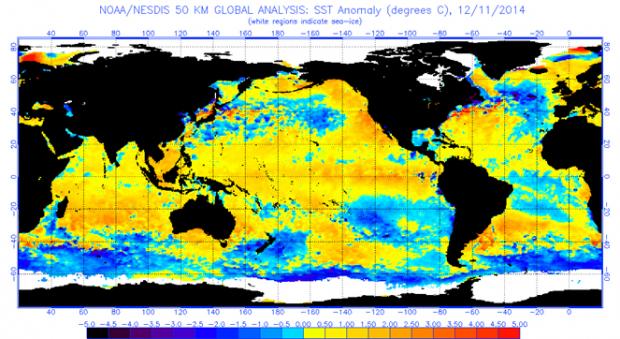
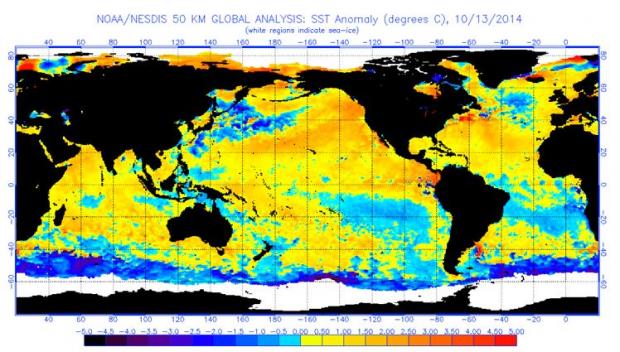
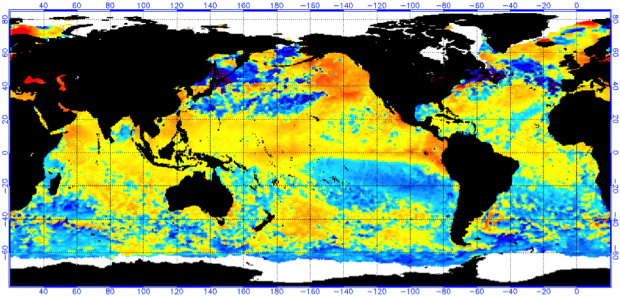
As we have mentioned in our past evaluations of the El Niño’s significance in the summer and fall, we are back again to analyze the wintertime impacts of a developing El Niño on New Jersey weather. An El Niño occurs when warmer-than-average waters exist in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, specifically near the equatorial latitudes. This warming is due to a weakening of winds moving to the west, which typically transport warmer waters to the western Pacific, permitting cooler water to upwell to the surface in the east. When these winds are weaker or if they reverse direction, warm water stays in the east. The warmer sea surface temperatures in the east and the altered atmospheric flow pattern create a new dynamic between the ocean and atmosphere. The newly formed interaction sets up distinct and repetitive weather patterns across the world. No two El Niño events are alike; they vary depending on the magnitude and location of where the largest temperature anomalies are found. However, each one tends to alter weather patterns outside the overall norm.